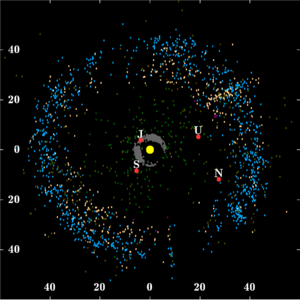
Kuiper belt
The Kuiper belt ( / ˈ k aɪ p ər / ), [1] occasionally called the Edgeworth–Kuiper belt , is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System , extending from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU ) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun . [2] It is similar to the asteroid belt , but is far larger—20 times as wide and 20 to 200 times as massive. [3] [4] Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small bodies or remnants from when the Solar System formed . While many asteroids are composed primarily of rock and metal, most Kuiper belt objects are composed largely of frozen volatiles (termed "ices"), such as methane , ammonia and water . The Kuiper belt is home to three officially recognized dwarf planets : Pluto , Haumea and Makemake . Some of the Solar System's moons , such as Neptune's Triton and Saturn 's Phoebe , may have originated in the region. [5] [6]
Page Revisions
| Year | Metadata | Sections | Top Words | First Paragraph |
| 2018 |
357629 characters 23 sections 63 paragraphs 28 images 471 internal links 255 external links |
kuiper 0.388 belt 0.380 objects 0.323 kbos 0.262 neptune 0.251 pluto 0.193 scattered 0.175 disc 0.150 au 0.126 orbits 0.125 kbo 0.113 object 0.102 comets 0.099 resonance 0.087 population 0.084 |
The Kuiper belt ( / ˈ k aɪ p ər / ), [1] occasionally called the Edgeworth–Kuiper belt , is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System , extending from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU ) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun . [2] It is similar to the asteroid belt , but is far larger—20 times as wide and 20 to 200 times as massive. [3] [4] Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small bodies or remnants from when the Solar System formed . While many asteroids are composed primarily of rock and metal, most Kuiper belt objects are composed largely of frozen volatiles (termed "ices"), such as methane , ammonia and water . The Kuiper belt is home to three officially recognized dwarf planets : Pluto , Haumea and Makemake . Some of the Solar System's moons , such as Neptune's Triton and Saturn 's Phoebe , may have originated in the region. [5] [6] |
|
| 2017 |
340160 characters 23 sections 61 paragraphs 26 images 460 internal links 239 external links |
kuiper 0.393 belt 0.385 objects 0.328 neptune 0.253 kbos 0.251 pluto 0.188 scattered 0.179 disc 0.153 orbits 0.128 au 0.124 kbo 0.106 object 0.104 comets 0.101 resonance 0.089 population 0.087 |
The Kuiper belt ( / ˈ k aɪ p ər / or Dutch pronunciation: ['kœy̯pǝr] ), [1] occasionally called the Edgeworth–Kuiper belt , is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System , extending from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU ) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun . [2] It is similar to the asteroid belt , but is far larger—20 times as wide and 20 to 200 times as massive. [3] [4] Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small bodies or remnants from when the Solar System formed . While many asteroids are composed primarily of rock and metal, most Kuiper belt objects are composed largely of frozen volatiles (termed "ices"), such as methane , ammonia and water . The Kuiper belt is home to three officially recognized dwarf planets : Pluto , Haumea and Makemake . Some of the Solar System's moons , such as Neptune's Triton and Saturn 's Phoebe , may have originated in the region. [5] [6] |
|
| 2016 |
343865 characters 23 sections 63 paragraphs 26 images 453 internal links 234 external links |
kuiper 0.387 belt 0.373 objects 0.324 kbos 0.268 neptune 0.258 pluto 0.184 scattered 0.174 disc 0.148 orbits 0.128 au 0.124 kbo 0.116 comets 0.101 object 0.101 population 0.097 resonance 0.089 |
The Kuiper belt / ˈ k aɪ p ər / or Dutch pronunciation: ['kœy̯pǝr] , [1] sometimes called the Edgeworth–Kuiper belt , is a circumstellar disc in the Solar System beyond the planets , extending from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU ) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun . [2] It is similar to the asteroid belt , but it is far larger—20 times as wide and 20 to 200 times as massive. [3] [4] Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small bodies , or remnants from the Solar System's formation. Although many asteroids are composed primarily of rock and metal, most Kuiper belt objects are composed largely of frozen volatiles (termed "ices"), such as methane , ammonia and water . The Kuiper belt is home to three officially recognized dwarf planets : Pluto , Haumea , and Makemake . Some of the Solar System's moons , such as Neptune's Triton and Saturn 's Phoebe , are also thought to have originated in the region. [5] [6] |
|
| 2015 |
301896 characters 22 sections 60 paragraphs 26 images 454 internal links 176 external links |
kuiper 0.429 belt 0.381 kbos 0.299 neptune 0.242 objects 0.239 pluto 0.206 scattered 0.174 disc 0.150 kbo 0.145 comets 0.123 orbits 0.121 au 0.109 object 0.107 oort 0.096 resonance 0.079 |
The Kuiper belt / ˈ k aɪ p ər / or /'køypǝr/ [1] (as in Dutch ), sometimes called the Edgeworth–Kuiper belt , is a circumstellar disc in the Solar System beyond the planets , extending from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU ) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun . [2] It is similar to the asteroid belt , but it is far larger—20 times as wide and 20 to 200 times as massive. [3] [4] Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small bodies , or remnants from the Solar System's formation. Although many asteroids are composed primarily of rock and metal, most Kuiper belt objects are composed largely of frozen volatiles (termed "ices"), such as methane , ammonia and water . The Kuiper belt is home to three officially recognized dwarf planets : Pluto , Haumea , and Makemake . Some of the Solar System's moons , such as Neptune's Triton and Saturn 's Phoebe , are also thought to have originated in the region. [5] [6] |
|
| 2014 |
281643 characters 22 sections 55 paragraphs 24 images 432 internal links 153 external links |
kuiper 0.443 belt 0.393 kbos 0.315 neptune 0.247 objects 0.227 pluto 0.193 scattered 0.178 disc 0.146 kbo 0.136 comets 0.125 orbits 0.123 au 0.105 oort 0.098 object 0.092 resonance 0.080 |
The Kuiper belt / ˈ k aɪ p ər / , sometimes called the Edgeworth–Kuiper belt , is a region of the Solar System beyond the planets , extending from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU ) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun . [1] It is similar to the asteroid belt , but it is far larger—20 times as wide and 20 to 200 times as massive. [2] [3] Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small bodies , or remnants from the Solar System's formation. Although most asteroids are composed primarily of rock and metal, most Kuiper belt objects are composed largely of frozen volatiles (termed "ices"), such as methane , ammonia and water. The Kuiper belt is home to at least three dwarf planets : Pluto , Haumea , and Makemake . Some of the Solar System's moons , such as Neptune's Triton and Saturn 's Phoebe , are also believed to have originated in the region. [4] [5] |
|
| 2013 |
278340 characters 22 sections 55 paragraphs 24 images 431 internal links 148 external links |
kuiper 0.436 belt 0.402 kbos 0.309 neptune 0.244 objects 0.230 pluto 0.190 scattered 0.180 kbo 0.138 disc 0.133 orbits 0.128 comets 0.115 au 0.106 object 0.097 edgeworth 0.095 oort 0.091 |
The Kuiper belt / ˈ k aɪ p ər / , sometimes called the Edgeworth–Kuiper belt (after the astronomers Kenneth Edgeworth and Gerard Kuiper ), is a region of the Solar System beyond the planets, extending from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU ) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun . [1] It is similar to the asteroid belt , but it is far larger—20 times as wide and 20 to 200 times as massive. [2] [3] Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small bodies , or remnants from the Solar System's formation. Although some asteroids are composed primarily of rock and metal, most Kuiper belt objects are composed largely of frozen volatiles (termed "ices"), such as methane , ammonia and water. The classical belt is home to at least three dwarf planets : Pluto , Haumea , and Makemake . Some of the Solar System's moons , such as Neptune's Triton and Saturn 's Phoebe , are also believed to have originated in the region. [4] [5] |
|
| 2012 |
275277 characters 22 sections 55 paragraphs 24 images 434 internal links 146 external links |
kuiper 0.434 belt 0.405 kbos 0.297 neptune 0.249 objects 0.217 scattered 0.192 pluto 0.183 disc 0.147 kbo 0.137 orbits 0.128 comets 0.114 object 0.106 au 0.106 oort 0.090 population 0.084 |
The Kuiper belt ( / [invalid input: 'icon'] ˈ k aɪ p ər / rhyming with "viper"), sometimes called the Edgeworth–Kuiper belt , is a region of the Solar System beyond the planets, extending from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU ) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun . [1] It is similar to the asteroid belt , but it is far larger—20 times as wide and 20 to 200 times as massive. [2] [3] Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small bodies , or remnants from the Solar System's formation. While most asteroids are composed primarily of rock and metal, most Kuiper belt objects [nb 2] are composed largely of frozen volatiles (termed "ices"), such as methane , ammonia and water. The classical belt is home to at least three dwarf planets : Pluto , Haumea , and Makemake . Some of the Solar System's moons , such as Neptune 's Triton and Saturn's Phoebe , are also believed to have originated in the region. [4] [5] |
|
| 2011 |
263077 characters 22 sections 54 paragraphs 23 images 424 internal links 131 external links |
kuiper 0.421 belt 0.400 kbos 0.304 neptune 0.239 objects 0.234 pluto 0.194 scattered 0.176 disc 0.141 kbo 0.133 orbits 0.127 comets 0.121 au 0.112 object 0.103 population 0.096 oort 0.096 |
The Kuiper belt ( / [invalid input: 'icon'] ˈ k aɪ p ər / , rhyming with "viper"), sometimes called the Edgeworth–Kuiper belt , is a region of the Solar System beyond the planets extending from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU ) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun . [1] It is similar to the asteroid belt , although it is far larger—20 times as wide and 20 to 200 times as massive. [2] [3] Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small bodies , or remnants from the Solar System's formation. While the asteroid belt is composed primarily of rock , ices, and metal, the Kuiper objects are composed largely of frozen volatiles (termed "ices"), such as methane , ammonia and water. The classical (low-eccentricity) belt is home to at least three dwarf planets : Pluto , Haumea , and Makemake . Some of the Solar System's moons , such as Neptune 's Triton and Saturn's Phoebe , are also believed to have originated in the region. [4] [5] |
|
| 2010 |
244205 characters 21 sections 53 paragraphs 22 images 422 internal links 95 external links |
kuiper 0.425 belt 0.399 kbos 0.307 objects 0.236 neptune 0.236 pluto 0.196 scattered 0.170 kbo 0.135 orbits 0.128 disc 0.127 comets 0.116 au 0.113 object 0.099 population 0.097 oort 0.097 |
The Kuiper belt ( pronounced /ˈkaɪpər/ (deprecated template) , rhyming with "viper"), [1] sometimes called the Edgeworth-Kuiper belt , is a region of the Solar System beyond the planets extending from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU ) to approximately 55 AU from the Sun . [2] It is similar to the asteroid belt , although it is far larger—20 times as wide and 20–200 times as massive. [3] [4] Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small bodies , or remnants from the Solar System's formation. While the asteroid belt is composed primarily of rock and metal , the Kuiper objects are composed largely of frozen volatiles (termed "ices"), such as methane , ammonia and water . The belt is home to at least three dwarf planets – Pluto , Haumea , and Makemake . Some of the Solar System's moons , such as Neptune 's Triton and Saturn's Phoebe , are also believed to have originated in the region. [5] [6] |
|
| 2009 |
233397 characters 21 sections 51 paragraphs 21 images 417 internal links 88 external links |
kuiper 0.421 belt 0.392 kbos 0.309 objects 0.233 neptune 0.231 pluto 0.203 scattered 0.171 kbo 0.148 orbits 0.129 disc 0.128 comets 0.116 au 0.114 object 0.100 population 0.097 oort 0.097 |
The Kuiper belt ( pronounced /ˈkaɪpər/ (deprecated template) , rhyming with "viper"), [1] sometimes called the Edgeworth-Kuiper belt , is a region of the Solar System beyond the planets extending from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU ) to approximately 55 AU from the Sun . [2] It is similar to the asteroid belt , although it is far larger—20 times as wide and 20–200 times as massive. [3] [4] Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small bodies , or remnants from the Solar System's formation. While the asteroid belt is composed primarily of rock and metal , the Kuiper belt objects are composed largely of frozen volatiles (termed "ices"), such as methane , ammonia and water . It is home to at least three dwarf planets – Pluto , Haumea and Makemake . |
|
| 2008 |
221866 characters 21 sections 51 paragraphs 19 images 416 internal links 84 external links |
kuiper 0.424 belt 0.395 kbos 0.304 objects 0.238 neptune 0.224 scattered 0.183 pluto 0.176 kbo 0.151 disc 0.131 orbits 0.128 au 0.116 comets 0.112 fernandez 0.104 object 0.102 oort 0.099 |
The Kuiper belt ( Template:PronEng , to rhyme with "viper"), [1] sometimes called the Edgeworth-Kuiper belt , is a region of the Solar System beyond the planets extending from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU ) to approximately 55 AU from the Sun . [2] It is similar to the asteroid belt , although it is far larger -- 20 times as wide and 20–200 times as massive. [3] [4] Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small bodies (remnants from the Solar System's formation). It is home to at least three dwarf planets – Pluto , Haumea and Makemake . But while the asteroid belt is composed primarily of rock and metal , the Kuiper belt objects are composed largely of frozen volatiles (dubbed "ices"), such as methane , ammonia and water . |
|
| 2007 |
195218 characters 22 sections 53 paragraphs 19 images 320 internal links 75 external links |
kuiper 0.428 belt 0.393 kbos 0.325 objects 0.237 neptune 0.204 pluto 0.188 scattered 0.152 kbo 0.150 comets 0.145 orbits 0.118 oort 0.117 au 0.109 disc 0.107 fernandez 0.104 object 0.101 |
The Kuiper belt ( Template:PronEng , to rhyme with "viper"), [1] sometimes called the Edgeworth-Kuiper belt , is a region of the Solar System beyond the planets extending from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU ) [2] to approximately 55 AU from the Sun . [3] It is similar to the asteroid belt , although it is far larger; 20 times as wide and 20–200 times as massive. [4] [5] Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small bodies (remnants from the Solar System's formation) and at least one dwarf planet – Pluto . But while the asteroid belt is composed primarily of rock and metal , the Kuiper belt objects are composed largely of frozen volatiles (dubbed "ices"), such as methane , ammonia and water . |
|
| 2006 |
86711 characters 15 sections 26 paragraphs 8 images 302 internal links 17 external links |
objects 0.428 belt 0.373 kuiper 0.364 kbo 0.191 neptune 0.188 resonance 0.133 au 0.126 kbos 0.122 plutinos 0.114 edgeworth 0.113 cubewanos 0.109 disk 0.101 quaoar 0.098 distribution 0.097 scattered 0.095 |
The Kuiper belt ( pronounced /ˈkaɪpɚ/ , to rhyme with 'viper') is an area of the solar system extending from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU ) to 50 AU from the Sun . |
|
| 2005 |
58805 characters 8 sections 18 paragraphs 3 images 274 internal links 8 external links |
belt 0.462 kuiper 0.400 kbos 0.268 objects 0.267 kbo 0.249 edgeworth 0.206 neptunian 0.123 trans 0.112 au 0.102 neptune 0.099 sized 0.091 quaoar 0.089 tnos 0.085 28978 0.069 fernandez 0.069 |
The Kuiper belt ( pronounced /ˈkaɪpɚ/ ) is an area of the solar system extending from within the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU ) to 50 AU from the Sun , at inclinations consistent with the ecliptic . |
|
| 2004 |
51422 characters 8 sections 14 paragraphs 2 images 274 internal links 3 external links |
belt 0.433 kbos 0.419 edgeworth 0.387 kuiper 0.275 objects 0.217 leonard 0.163 sedna 0.160 astronomers 0.108 qb1 0.104 charon 0.104 oort 0.101 neptune 0.092 kenneth 0.082 cloud 0.076 infrared 0.074 |
The Kuiper belt ("KYE per") is an area of the solar system extending from within the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU ) to 50 AU from the sun , at inclinations consistent with the ecliptic . |
|
| 2003 |
11196 characters 1 sections 12 paragraphs 0 images 68 internal links 4 external links |
kbos 0.522 belt 0.339 edgeworth 0.268 blackbody 0.268 objects 0.255 kuiper 0.208 infrared 0.102 radiation 0.098 pluto 0.097 neptune 0.096 charon 0.096 astronomers 0.090 fernandez 0.089 wavelength 0.086 diameters 0.084 |
The Kuiper belt (sometimes called the Edgeworth belt or Edgeworth-Kuiper belt ) is an area of the solar system extending from within the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU ) to 50 AU from the sun . |
|
| 2002 |
4190 characters 1 sections 9 paragraphs 0 images 18 internal links 2 external links |
kuiper 0.570 belt 0.465 kbos 0.239 objects 0.159 pluto 0.133 neptune 0.132 charon 0.131 oort 0.128 inner 0.113 lumps 0.111 object 0.103 simulations 0.102 didn 0.095 performs 0.095 comets 0.093 |
The Kuiper Belt is an area of the solar system extending outwards from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU ) to 50 AU. |
|
| 2001 |
1999 characters 0 sections 4 paragraphs 0 images 7 internal links 2 external links |
kuiper 0.310 au 0.298 outwards 0.244 progressively 0.244 belt 0.234 object 0.224 1200 0.223 charon 0.214 objects 0.207 unclear 0.199 links 0.196 classification 0.191 neptunian 0.179 external 0.176 fairly 0.173 |
The Kuiper Belt is an area of the solar system extending outwards from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU ) to 50 AU . The largest of the objects are the planet Pluto and its moon Charon . A new Kuiper belt object, currently called 2001 KX76, has been found that is just slightly smaller, with a diameter near 1200 km. Other objects are progressively smaller. The exact classification of these is unclear, since they are probably fairly different from the asteroids of the inner solar system. |